Erectile function is a complex physiological process that involves the coordination of multiple systems within the body, including the nervous system, circulatory system, and hormonal balance. At its core, an erection occurs when blood flows into the corpora cavernosa, two sponge-like chambers in the penis, causing it to expand and harden. This process is triggered by sexual stimulation, which activates nerve pathways that signal the release of nitric oxide (NO), a molecule that relaxes smooth muscle cells in blood vessels. This relaxation allows blood to flow into the penile tissues, increasing pressure and resulting in an erection. However, the ability to achieve and maintain an erection is influenced by a combination of biological, psychological, and lifestyle factors, making it a multifaceted topic that requires a nuanced understanding.
Understanding Erectile Function and Its Biological Foundations
One of the key biological mechanisms underpinning erectile function is the role of nitric oxide. When sexual stimulation occurs, the brain sends signals through the spinal cord to the nerves in the penis, prompting the release of nitric oxide. This molecule diffuses into the smooth muscle cells of the corpora cavernosa, activating an enzyme called guanylate cyclase. This enzyme converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) into cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which further relaxes the smooth muscle cells, allowing blood vessels to dilate. The increased blood flow leads to the engorgement of the penile tissues, creating an erection. However, the body has a natural mechanism to reverse this process: phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) enzymes break down cGMP, reducing its concentration and allowing the smooth muscles to contract, thereby decreasing blood flow and ending the erection.
While the physiological process of achieving an erection is well-documented, the maintenance of erectile hardness is equally critical. Factors such as vascular health, hormonal balance, and neurological function play a significant role in ensuring that the erection remains firm and sustained. For example, individuals with conditions like atherosclerosis, which narrows blood vessels, may struggle with achieving or maintaining an erection due to reduced blood flow. Similarly, hormonal imbalances, particularly low testosterone levels, can impair libido and erectile function. Understanding these biological foundations is essential for developing effective strategies to enhance erectile hardness, whether through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, or targeted supplements.
The Medical Perspective: Clinical Studies and Pharmacological Insights
From a medical standpoint, the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) has evolved significantly over the past few decades, with a growing emphasis on evidence-based interventions. Clinical studies have played a pivotal role in identifying the most effective pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches to improving erectile hardness. One of the most widely prescribed medications for ED is sildenafil (Viagra), which works by inhibiting PDE5, thereby prolonging the effects of cGMP and allowing for sustained blood flow into the penile tissues. Clinical trials have demonstrated that sildenafil is effective in approximately 70-80% of men with ED, with minimal side effects when used as directed.
Other pharmacological options include tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), and avanafil (Stendra), which all function similarly to sildenafil by inhibiting PDE5. These medications are typically taken on an as-needed basis, with dosing regimens tailored to individual patient needs. However, it is important to note that these drugs are not a cure for ED but rather a temporary solution that addresses the physiological aspects of the condition. For men with underlying health issues such as diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease, these medications may be combined with lifestyle modifications or other therapies to achieve optimal results.
Recent advancements in medical research have also explored the potential of combination therapies for ED. For example, studies have shown that the integration of PDE5 inhibitors with testosterone replacement therapy may be beneficial for men with both ED and low testosterone levels. Additionally, the role of vascular health in ED has led to the development of treatments that focus on improving blood flow, such as endothelial function-enhancing drugs or lifestyle interventions that promote cardiovascular health. These approaches highlight the importance of a holistic medical perspective in addressing the multifactorial nature of erectile dysfunction.
The Psychological Dimension: Mental Health and Erectile Performance
While the biological mechanisms of erectile function are well-established, the psychological factors influencing sexual performance cannot be overlooked. Erectile dysfunction is often intertwined with mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and stress, which can significantly impact a man’s ability to achieve and maintain an erection. Psychological factors may account for up to 30% of ED cases, according to some studies, underscoring the need for a comprehensive approach that addresses both physical and emotional well-being.
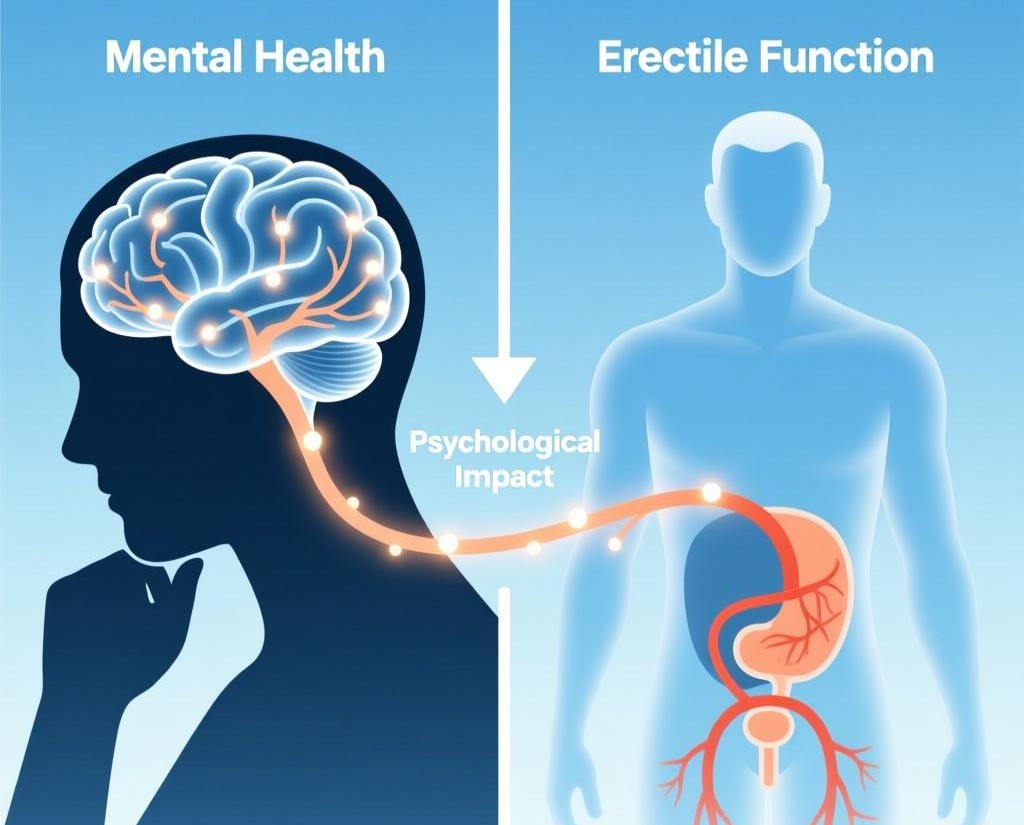
Stress, in particular, plays a critical role in erectile performance. Chronic stress can lead to the release of cortisol, a hormone that may interfere with the body’s ability to produce nitric oxide and maintain adequate blood flow to the penis. Additionally, stress can disrupt the brain’s ability to send signals to the nerves involved in sexual arousal, creating a cycle of anxiety and performance pressure. This phenomenon, often referred to as “performance anxiety,” can exacerbate ED, making it a self-fulfilling prophecy. Men experiencing such anxiety may benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or other psychological interventions designed to address negative thought patterns and reduce stress levels.
Depression is another psychological factor that can contribute to ED. Low mood and lack of interest in sexual activity are common symptoms of depression, which can lead to decreased libido and difficulty achieving an erection. In such cases, treating the underlying depression through medication, therapy, or lifestyle changes may improve erectile function. However, it is important to note that the relationship between depression and ED is bidirectional: ED can also contribute to feelings of sadness, low self-esteem, and relationship strain, further worsening mental health. This interplay highlights the importance of addressing both psychological and physiological factors in the treatment of ED.
Lifestyle Factors and Their Impact on Erectile Function
Emerging research has increasingly emphasized the role of lifestyle factors in maintaining healthy erectile function. While pharmacological and psychological interventions are essential, many experts argue that sustainable improvements in erectile hardness often stem from long-term lifestyle changes. Factors such as diet, physical activity, sleep quality, and substance use can significantly influence vascular health, hormonal balance, and overall sexual performance.
Diet plays a crucial role in erectile health, as certain nutrients are known to support vascular function and nitric oxide production. For example, foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, can help reduce oxidative stress, which is linked to endothelial dysfunction. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and mackerel, have also been shown to improve blood flow and reduce inflammation, both of which are beneficial for erectile function. Conversely, diets high in processed foods, saturated fats, and sugar can contribute to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, all of which are risk factors for ED.
Physical activity is another key lifestyle factor that impacts erectile health. Regular exercise, particularly aerobic activities such as running, swimming, or cycling, can improve cardiovascular fitness, enhance blood circulation, and promote the release of endorphins, which can reduce stress and improve mood. Strength training and pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegels, are also beneficial, as they can enhance muscle tone and improve control over ejaculation. However, it is important to note that excessive exercise or overtraining can have the opposite effect, leading to fatigue and decreased libido. Therefore, a balanced exercise routine is essential for optimal sexual health.
Nutritional Supplements and Their Role in Enhancing Erectile Hardness
As the demand for natural and alternative solutions to erectile dysfunction grows, nutritional supplements have become a popular topic of discussion. These supplements are often marketed as “natural” or “herbal” remedies, but their effectiveness and safety can vary widely. While some ingredients have been scientifically validated for their role in improving erectile function, others lack sufficient evidence to support their claims. Understanding the science behind these supplements is essential for making informed decisions about their use.
One of the most commonly studied supplements for erectile health is L-arginine, an amino acid that serves as a precursor to nitric oxide. Clinical trials have shown that L-arginine supplementation can improve blood flow and enhance erectile function in men with mild to moderate ED. However, the effects of L-arginine may be more pronounced in individuals with underlying vascular issues, and its efficacy can vary depending on dosage and individual physiology. Another popular supplement is ginseng, which has been traditionally used in Chinese medicine to boost energy and libido. Some studies suggest that ginseng may improve erectile function by enhancing nitric oxide production and reducing oxidative stress, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Other supplements that have garnered attention include D-Aspartic acid, which is believed to increase testosterone levels, and pomegranate extract, which is rich in antioxidants and may improve endothelial function. While these supplements show promise, it is important to recognize that their effectiveness is often not well-established in large-scale clinical trials. Additionally, some supplements may interact with prescription medications, such as PDE5 inhibitors, or may have side effects that range from mild to severe. As a result, individuals considering these supplements should consult with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe and appropriate for their specific needs.
The Role of Hormones in Erectile Health
Hormonal balance is a critical factor in maintaining healthy erectile function, with testosterone being the most well-known hormone involved. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a multifaceted role in sexual health, including the regulation of libido, the maintenance of erectile function, and the production of sperm. Low testosterone levels, often referred to as hypogonadism, can lead to decreased sexual desire, difficulty achieving an erection, and reduced overall energy levels. However, the relationship between testosterone and erectile function is complex, as other hormones and physiological factors also contribute to sexual performance.
In addition to testosterone, other hormones such as estrogen, prolactin, and cortisol can influence erectile health. While estrogen is primarily associated with female physiology, it also plays a role in male sexual function by supporting vascular health and maintaining the integrity of the penile tissues. Prolactin, which is released after orgasm, can affect sexual desire and may contribute to the refractory period—the time between orgasms during which a man is less responsive to sexual stimulation. Cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, can interfere with the production of testosterone and may exacerbate erectile dysfunction when present in excess.
For men experiencing symptoms of low testosterone, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be a viable option. However, HRT is not without risks, including potential side effects such as acne, fluid retention, and cardiovascular complications. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether HRT is appropriate and to monitor its effects closely. In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can help support healthy hormone levels and improve erectile function.
The Science of Nitric Oxide and Its Connection to Erectile Function
Nitric oxide (NO) is a key molecule in the process of achieving and maintaining an erection, and its role in erectile function has been extensively studied. As the primary mediator of penile erection, NO is responsible for relaxing the smooth muscle cells in the corpora cavernosa, allowing blood to flow into the penile tissues. This process is initiated by sexual stimulation, which triggers the release of NO from the endothelial cells lining the blood vessels. Once released, NO diffuses into the smooth muscle cells, where it activates the enzyme guanylate cyclase, leading to the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). This molecule then causes the smooth muscles to relax, allowing the blood vessels to dilate and increasing blood flow into the penis.
While the role of NO in erectile function is well-established, the production and regulation of this molecule are influenced by a variety of factors. For instance, endothelial dysfunction, a condition in which the inner lining of blood vessels fails to release adequate amounts of NO, is a common underlying cause of ED. This dysfunction can result from conditions such as atherosclerosis, diabetes, and hypertension, all of which impair the body’s ability to produce and utilize NO effectively. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as smoking, poor diet, and sedentary behavior can contribute to endothelial dysfunction by promoting oxidative stress and inflammation, which further hinder NO production.
Supplements and medications that enhance NO production or improve its bioavailability are often marketed as solutions for ED. For example, L-arginine, which is a precursor to NO, is frequently included in supplements aimed at improving erectile function. Similarly, medications like sildenafil (Viagra) work by inhibiting PDE5, which allows cGMP to remain active for a longer period, thereby prolonging the effects of NO. However, the effectiveness of these interventions can vary, and it is important to note that NO production is just one piece of the complex puzzle of erectile health. A holistic approach that addresses multiple factors, including vascular health, hormonal balance, and psychological well-being, is essential for achieving optimal results.
The Importance of Blood Flow in Maintaining Erectile Hardness
Blood flow is one of the most critical components of achieving and maintaining an erection, and its role in erectile hardness cannot be overstated. The process of an erection relies on the ability of blood to flow into the corpora cavernosa, which are the spongy tissues in the penis. When sexual stimulation occurs, the brain sends signals to the nerves in the penis, prompting the release of nitric oxide, which relaxes the smooth muscle cells in the blood vessels. This relaxation allows blood to flow into the penile tissues, increasing pressure and creating an erection. However, the maintenance of erectile hardness depends on the continued flow of blood into the penis and the ability to sustain this flow throughout the duration of sexual activity.
Conditions that impair blood flow, such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes, are significant risk factors for erectile dysfunction. Atherosclerosis, which involves the buildup of plaque in the arteries, can narrow blood vessels and reduce the amount of blood that reaches the penile tissues. Similarly, hypertension can damage the endothelial lining of blood vessels, leading to endothelial dysfunction and impaired NO production. Diabetes, which is associated with chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, can also contribute to vascular damage, further complicating the ability to achieve and maintain an erection. These conditions highlight the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health as a key strategy for preserving erectile function.
Improving blood flow to the penis can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. For example, regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercise, can enhance cardiovascular health and promote better blood circulation. A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and other nutrients can also support vascular function and reduce inflammation. In addition, medications such as PDE5 inhibitors can help improve blood flow by prolonging the effects of nitric oxide. However, it is important to recognize that blood flow is just one aspect of erectile health, and a comprehensive approach that addresses multiple factors is necessary for long-term success.
The Impact of Age on Erectile Function and the Role of Supplements
As men age, the natural decline in testosterone levels and the gradual deterioration of vascular health can significantly impact erectile function. While age-related changes in sexual performance are common, they are not an inevitable consequence of aging, and many older men can maintain healthy erections through lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and targeted supplements. Understanding how aging affects erectile function and the potential role of supplements in mitigating these effects is essential for developing effective strategies to enhance sexual health.
One of the primary factors contributing to age-related erectile dysfunction is the decline in testosterone production. Testosterone levels typically decrease by about 1-2% per year after the age of 30, which can lead to reduced libido, decreased sexual desire, and difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection. Additionally, the aging process can impair the function of the endothelial cells, which are responsible for producing nitric oxide. This decline in NO production can reduce the ability to achieve an erection, even in the presence of adequate sexual stimulation. Furthermore, the cumulative effects of chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease can exacerbate these age-related changes, making it more challenging to maintain erectile hardness.
Supplements designed to support erectile function in older men often focus on enhancing nitric oxide production, improving blood flow, and supporting hormonal balance. Ingredients such as L-arginine, L-citrulline, and pomegranate extract are frequently included in these supplements due to their potential to improve vascular health and promote better blood circulation. However, the effectiveness of these supplements can vary, and it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new regimen. In addition to supplements, lifestyle interventions such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can play a crucial role in maintaining sexual health as men age.
The Debate Over Natural vs. Synthetic Supplements
The market for supplements aimed at improving erectile function is vast and diverse, with products ranging from natural herbal remedies to synthetic formulations. This diversity has led to an ongoing debate about the efficacy, safety, and regulatory oversight of these supplements. While some natural ingredients have been scientifically validated for their role in enhancing erectile health, others lack sufficient evidence to support their claims. Similarly, synthetic supplements, such as PDE5 inhibitors, are often more rigorously tested and regulated, but they may come with a higher risk of side effects. Understanding the differences between natural and synthetic supplements is essential for making informed decisions about their use.

Natural supplements are typically derived from plants, herbs, or other organic sources and are often marketed as “safe” or “gentle” alternatives to pharmaceutical treatments. Ingredients such as ginseng, ashwagandha, and fenugreek are frequently cited for their potential to improve sexual function and libido. However, the scientific evidence supporting these claims is often limited, with many studies relying on small sample sizes or anecdotal reports rather than rigorous clinical trials. Additionally, the potency and consistency of natural supplements can vary widely, making it difficult to assess their effectiveness or safety.
In contrast, synthetic supplements are generally produced in controlled environments and undergo more stringent testing for purity and potency. PDE5 inhibitors, such as sildenafil and tadalafil, are examples of synthetic supplements that have been extensively studied and are approved for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. These medications are effective in the majority of cases and are often prescribed by healthcare providers. However, they may come with side effects such as headaches, flushing, and gastrointestinal discomfort, and their use is typically limited to men with specific medical conditions or under the guidance of a physician.
The Future of Erectile Health: Emerging Trends and Research
As research into erectile health continues to evolve, new trends and innovations are emerging that may revolutionize the way we approach sexual function and performance. From advancements in biotechnology to the development of novel therapeutic approaches, the future of erectile health is likely to be shaped by a combination of scientific breakthroughs and a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between physiology, psychology, and lifestyle factors.
One of the most promising areas of research is the development of gene therapy and regenerative medicine for erectile dysfunction. Scientists are exploring ways to stimulate the production of nitric oxide or enhance the function of endothelial cells through genetic interventions. For example, studies are underway to investigate the potential of gene therapy to repair damaged blood vessels and improve vascular function in men with ED. Additionally, regenerative medicine techniques, such as stem cell therapy, are being explored as a means to regenerate damaged tissues and improve sexual function. While these approaches are still in the early stages of research, they represent a potential paradigm shift in the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
Another emerging trend is the integration of digital health technologies into the management of erectile health. Mobile applications and wearable devices are being developed to monitor physiological parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, and stress levels, providing users with real-time feedback on their sexual health. These technologies can also be used to track the effectiveness of supplements or medications, allowing for personalized adjustments to treatment plans. Furthermore, telemedicine platforms are enabling men to consult with healthcare providers remotely, making it easier to access medical advice and support for sexual health concerns.
As the field of erectile health continues to advance, it is clear that a multidisciplinary approach will be essential for addressing the complex factors that contribute to sexual function. By combining scientific research, medical interventions, psychological support, and lifestyle modifications, men can take proactive steps to enhance their sexual health and maintain erectile hardness. The future of erectile health is likely to be defined by a greater emphasis on personalized medicine, technological innovation, and a holistic understanding of the factors that influence sexual performance. As such, staying informed about the latest developments in this field will be crucial for making the most effective choices in the pursuit of sexual well-being.
