Understanding Viagra and Its Mechanism
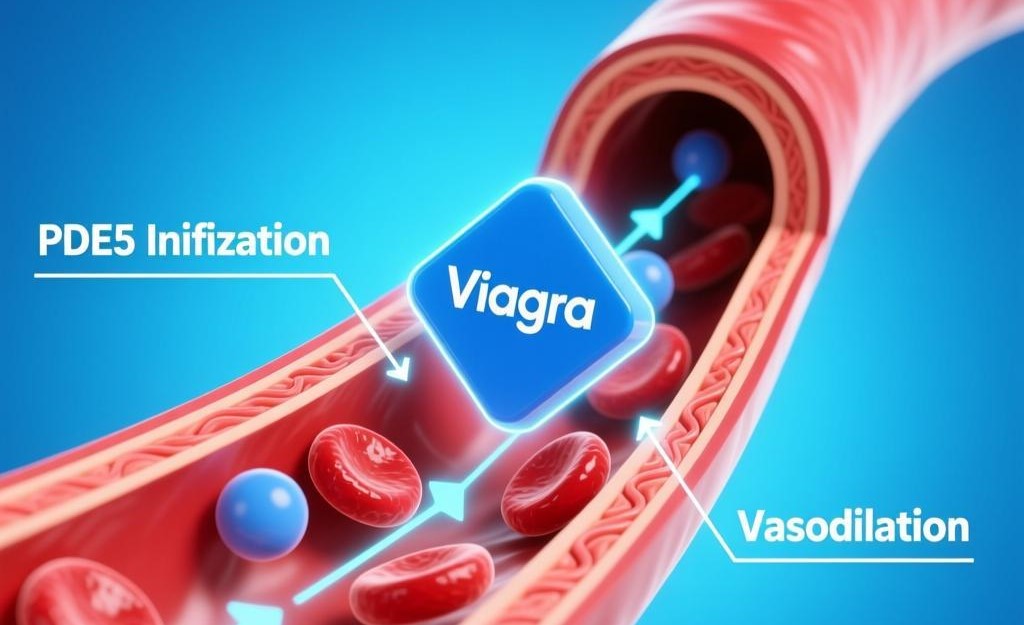
Viagra, generically known as sildenafil, is a widely prescribed medication primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. Developed by Pfizer, Viagra works by inhibiting the enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), which is responsible for breaking down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). This inhibition allows cGMP to accumulate, leading to relaxation of smooth muscle in the penile corpus cavernosum and increased blood flow, facilitating an erection. While its primary use is for ED, Viagra has also been approved for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. The mechanism of action for PAH is similar, as sildenafil helps dilate blood vessels, reducing the workload on the heart and improving blood flow.
Viagra is typically taken orally, with the dosage and frequency depending on the condition being treated. For ED, the standard dose is 50 mg, taken approximately 30 to 60 minutes before sexual activity. However, the dosage may be adjusted based on individual response and tolerability. For PAH, the dosage is generally higher, often starting at 20 mg twice daily. It is important to note that Viagra is not a cure for ED or PAH but rather a tool to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Patients are often advised to use Viagra in conjunction with lifestyle modifications and other treatments as recommended by their healthcare provider.
Despite its efficacy, Viagra is not without risks. One of the most significant concerns is its potential impact on cardiovascular health. The drug’s ability to lower blood pressure can be beneficial for some patients, but it may also pose risks for those with preexisting cardiovascular conditions. Understanding the interplay between Viagra and the cardiovascular system is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to ensure safe and effective use of the medication.
Cardiovascular Risks and Viagra
Viagra’s primary mechanism of action—vasodilation—can have profound effects on the cardiovascular system. While this property is beneficial for conditions like PAH, it can also pose risks for patients with underlying cardiovascular disease. The most critical concern is the potential for sildenafil to cause hypotension (low blood pressure), particularly in patients who are already taking medications that lower blood pressure, such as nitrates, alpha-blockers, or beta-blockers. When combined with these medications, Viagra can lead to a dangerous drop in blood pressure, potentially resulting in dizziness, fainting, or even cardiac arrest.
Another significant risk is the interaction between Viagra and nitrate medications. Nitrates, such as nitroglycerin, are commonly used to treat angina (chest pain) and heart failure. When combined with sildenafil, these drugs can cause a severe and potentially life-threatening drop in blood pressure. This interaction is so serious that patients taking nitrates are explicitly warned against using Viagra. The combination can lead to symptoms such as headache, nausea, and in extreme cases, syncope (loss of consciousness) or shock.
Additionally, Viagra can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. In patients with heart failure or coronary artery disease, the drug’s vasodilatory effects may reduce cardiac output, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, or palpitations. While these effects are generally mild, they can be exacerbated in patients with severe cardiovascular conditions. It is also worth noting that Viagra may not be suitable for patients with certain types of heart disease, such as those with unstable angina or recent myocardial infarction (heart attack), due to the potential for adverse cardiovascular events.
Research into the cardiovascular risks of Viagra has yielded mixed results. Some studies suggest that the drug may have a protective effect on the cardiovascular system by improving endothelial function and reducing oxidative stress. However, other studies highlight the potential for sildenafil to increase the risk of cardiovascular events in certain patient populations. For example, a 2017 study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that men with a history of cardiovascular disease who used Viagra had a higher risk of heart attack or stroke compared to those who did not use the medication. These findings underscore the importance of careful patient selection and monitoring when prescribing Viagra.
Medical Perspective: Balancing Benefits and Risks
From a medical standpoint, the use of Viagra requires a careful balance between its therapeutic benefits and the potential cardiovascular risks. Healthcare providers must assess each patient’s individual risk profile before prescribing the medication. This involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, current medications, and existing cardiovascular conditions. For patients with a history of heart disease, hypertension, or other risk factors, the benefits of Viagra may be outweighed by the potential dangers.
One of the key considerations in medical practice is the interaction between Viagra and other medications. Patients taking nitrates, alpha-blockers, or beta-blockers are at a heightened risk of adverse cardiovascular events when using sildenafil. These interactions are so well-documented that they are included in the drug’s prescribing information. However, some patients may not be aware of these risks, particularly if they are using over-the-counter medications or herbal supplements that contain nitrates or other vasodilators. Healthcare providers must educate patients about these interactions and ensure that they are not taking any contraindicated medications.
Another important factor is the patient’s age and overall cardiovascular health. While Viagra is generally considered safe for men over the age of 18, older patients may be at a higher risk of cardiovascular complications. Age-related changes in the cardiovascular system, such as reduced cardiac reserve and increased arterial stiffness, can make older patients more susceptible to the hypotensive effects of sildenafil. Additionally, patients with a history of stroke, peripheral artery disease, or other vascular conditions may require special consideration when using Viagra.
Healthcare providers must also be vigilant about the potential for sildenafil to exacerbate existing cardiovascular conditions. For example, in patients with heart failure, the drug’s vasodilatory effects may reduce cardiac output, leading to symptoms such as fatigue and shortness of breath. In patients with coronary artery disease, the medication may increase the risk of myocardial ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart muscle) by reducing coronary perfusion. These risks highlight the importance of regular monitoring and follow-up for patients on Viagra, particularly those with preexisting cardiovascular conditions.
Despite these risks, Viagra remains a valuable treatment option for many patients. Its ability to improve sexual function and enhance quality of life is well-documented, and for some patients, the benefits of the medication outweigh the potential cardiovascular risks. However, healthcare providers must remain cautious and ensure that patients are fully informed about the risks and benefits of Viagra. This includes discussing alternative treatment options, such as lifestyle modifications, psychological counseling, or other medications, to provide a comprehensive approach to managing ED or PAH.
Patient Perspective: Navigating the Risks
For patients, the use of Viagra involves a complex interplay between personal health, lifestyle choices, and the potential risks associated with the medication. While many patients experience significant improvements in their sexual function and overall quality of life, others may face challenges related to cardiovascular health. Understanding these risks is essential for making informed decisions about medication use and maintaining overall well-being.

One of the most critical concerns for patients is the potential for Viagra to interact with other medications. Patients taking nitrates, alpha-blockers, or beta-blockers may experience severe hypotension when using sildenafil, which can lead to dizziness, fainting, or even cardiac arrest. It is crucial for patients to disclose all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, to their healthcare providers. This transparency helps prevent dangerous interactions and ensures that the medication is used safely.
Patients with preexisting cardiovascular conditions must also be particularly cautious. Those with a history of heart disease, hypertension, or stroke may need to avoid Viagra altogether or use it under strict medical supervision. It is important for patients to understand that while Viagra can improve sexual function, it is not a substitute for addressing underlying cardiovascular health. Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can play a significant role in reducing cardiovascular risk and enhancing the effectiveness of Viagra.
Another challenge for patients is the potential for side effects. Common side effects of Viagra include headache, flushing, indigestion, and nasal congestion. While these are generally mild and temporary, they can be more severe in patients with certain medical conditions. For example, patients with hypertension may experience a more pronounced drop in blood pressure, which can be dangerous if not monitored closely. Patients should be advised to report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider immediately.
Patients must also be aware of the importance of regular follow-up with their healthcare provider. Even if Viagra is initially effective, long-term use may require adjustments in dosage or the introduction of additional treatments. Regular check-ups can help monitor cardiovascular health and ensure that the medication is not contributing to any adverse effects. Patients should also be encouraged to maintain open communication with their healthcare provider about their concerns and experiences with Viagra.
Healthcare Provider’s Role in Risk Management
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in ensuring the safe and effective use of Viagra, particularly in patients with cardiovascular conditions. Their responsibilities include comprehensive patient assessment, education, and ongoing monitoring to mitigate potential risks. A proactive approach is essential to balance the therapeutic benefits of Viagra with the need to protect patients from cardiovascular complications.
One of the first steps in risk management is a thorough patient evaluation. This includes a detailed medical history, assessment of current medications, and evaluation of cardiovascular risk factors. Healthcare providers must be particularly vigilant in identifying patients who may be at higher risk for adverse effects, such as those with a history of heart disease, hypertension, or the use of contraindicated medications. For example, patients taking nitrates or alpha-blockers should be counseled against using Viagra and alternative treatments should be explored.
Education is another critical component of risk management. Patients must be informed about the potential cardiovascular risks associated with Viagra, including the interaction with nitrates, the risk of hypotension, and the importance of monitoring for symptoms such as dizziness or fainting. Providers should also emphasize the importance of disclosing all medications and supplements to avoid dangerous interactions. Additionally, patients should be educated on the proper use of Viagra, including dosage, timing, and potential side effects.
Ongoing monitoring is essential to ensure that patients using Viagra remain safe and that the medication is effective. For patients with preexisting cardiovascular conditions, regular follow-up visits can help assess the impact of Viagra on their heart health. Blood pressure monitoring, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and other diagnostic tests may be necessary to detect any adverse effects early. Providers should also be prepared to adjust the dosage or discontinue Viagra if significant cardiovascular risks are identified.
Healthcare providers must also consider the broader context of a patient’s health when prescribing Viagra. This includes evaluating lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management, which can influence both the effectiveness of Viagra and overall cardiovascular health. Providers should encourage patients to adopt healthy habits that complement the medication, such as regular physical activity, a heart-healthy diet, and smoking cessation. These lifestyle modifications can reduce cardiovascular risk and enhance the benefits of Viagra.
Regulatory and Pharmaceutical Perspectives
From a regulatory and pharmaceutical standpoint, the use of Viagra is governed by strict guidelines to ensure patient safety and efficacy. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have established comprehensive frameworks for the approval, monitoring, and use of sildenafil. These guidelines are designed to balance the therapeutic benefits of Viagra with the potential cardiovascular risks, ensuring that patients receive the safest and most effective treatment possible.
The FDA’s approval process for Viagra included extensive clinical trials to assess its safety and efficacy. These trials focused on both the primary indication (ED) and the secondary indication (PAH), with particular attention to cardiovascular safety. For example, the approval of Viagra for PAH was based on studies that demonstrated its ability to improve exercise capacity and reduce pulmonary artery pressure without causing significant cardiovascular complications. However, the FDA also issued warnings about the potential risks associated with Viagra, particularly in patients with preexisting cardiovascular conditions.
Pharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer, are required to conduct post-market surveillance to monitor the long-term effects of Viagra. This includes tracking adverse events reported by patients and healthcare providers, as well as conducting additional studies to assess the drug’s safety profile. The pharmaceutical industry has also been proactive in addressing concerns about cardiovascular risks, with some companies conducting research to explore the potential protective effects of sildenafil on the cardiovascular system.
Regulatory agencies have also emphasized the importance of patient education and informed consent. Patients must be made aware of the potential risks and benefits of Viagra, including the contraindications related to nitrates and other medications. Regulatory guidelines also require that healthcare providers receive training on the proper use of Viagra and the management of cardiovascular risks. This ensures that patients are prescribed the medication safely and that any adverse effects are promptly addressed.
In addition to regulatory oversight, pharmaceutical companies have a responsibility to engage in ongoing research to improve the safety profile of Viagra. This includes exploring alternative formulations or dosing strategies that may reduce cardiovascular risks while maintaining the drug’s efficacy. For example, some studies have investigated the use of lower doses of sildenafil in patients with cardiovascular conditions, as well as the potential for combination therapies that may mitigate adverse effects.
Lifestyle and Complementary Strategies
While Viagra can be an effective treatment for ED and PAH, it is not a standalone solution. Patients are encouraged to adopt lifestyle and complementary strategies to enhance the benefits of the medication and reduce cardiovascular risks. These strategies include dietary modifications, regular physical activity, stress management, and the avoidance of harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Diet plays a crucial role in cardiovascular health and can influence the effectiveness of Viagra. A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can improve blood flow and reduce the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions. Patients should also limit their intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium, as these can contribute to arterial stiffness and increase the risk of heart disease. Incorporating foods high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, may also help protect the cardiovascular system and enhance the benefits of Viagra.
Regular physical activity is another essential component of cardiovascular health. Exercise improves blood circulation, strengthens the heart muscle, and helps regulate blood pressure. Patients should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, as recommended by the American Heart Association. Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, and swimming can be particularly beneficial for patients with ED, as they can improve overall sexual function and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Stress management is also important for patients using Viagra. Chronic stress can contribute to hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions, which may exacerbate the risks associated with the medication. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being. Patients should also be encouraged to seek psychological support if they are experiencing anxiety or depression, as these conditions can affect sexual function and cardiovascular health.
Finally, patients should avoid harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces blood flow, which can counteract the benefits of Viagra. Excessive alcohol use can also lead to hypertension and other cardiovascular issues, making it more difficult to manage the risks associated with the medication. By adopting a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes and complementary strategies, patients can significantly improve their cardiovascular health and enhance the effectiveness of Viagra.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Safety and Awareness
The use of Viagra presents a complex interplay between therapeutic benefits and cardiovascular risks. While the medication is highly effective for treating ED and PAH, its potential impact on the cardiovascular system requires careful consideration. Patients, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies must work together to ensure that the medication is used safely and effectively, with a focus on individualized care and comprehensive risk management.
For patients, the key to safe Viagra use lies in understanding the medication’s mechanism of action, recognizing potential interactions, and adopting lifestyle strategies that support cardiovascular health. Open communication with healthcare providers is essential to address concerns, monitor for adverse effects, and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans. Patients must also be proactive in managing their overall health, as lifestyle choices can significantly influence the effectiveness and safety of Viagra.
Healthcare providers play a critical role in assessing cardiovascular risk, educating patients about potential interactions, and ensuring that Viagra is prescribed appropriately. Regular monitoring and follow-up visits are necessary to detect any adverse effects early and to adjust treatment as needed. Providers should also consider the broader context of a patient’s health, including lifestyle factors and comorbid conditions, to provide a holistic approach to care.
From a regulatory and pharmaceutical perspective, ongoing research and post-market surveillance are essential to ensure the long-term safety and efficacy of Viagra. Regulatory agencies and pharmaceutical companies must continue to collaborate to address emerging risks and explore new strategies for improving patient outcomes. This includes investing in research to better understand the cardiovascular effects of sildenafil and developing alternative treatments that may reduce risks while maintaining therapeutic benefits.
Ultimately, the safe and effective use of Viagra requires a multifaceted approach that prioritizes patient safety, informed decision-making, and comprehensive care. By working together, patients, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies can ensure that Viagra remains a valuable treatment option while minimizing the potential risks associated with its use. A holistic approach that integrates medical, lifestyle, and regulatory considerations will continue to be essential in promoting cardiovascular health and enhancing the quality of life for patients using Viagra.
